How is Ethanol Produced Synthetically?
Ethanol, often referred to as alcohol, is a versatile chemical compound that plays a crucial role in various industries, from fuel production to pharmaceuticals. While most people are familiar with ethanol as the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, its synthetic production is a fascinating process that combines chemistry, engineering, and a bit of ingenuity. So, how is ethanol produced synthetically? Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to understand, and along the way, we’ll explore some interesting tools and techniques, like the use of a borosilicate glass reactor.
The Basics of Synthetic Ethanol Production
First things first: what exactly is synthetic ethanol? Unlike bioethanol, which is produced through the fermentation of sugars by yeast, synthetic ethanol is created through chemical reactions. The most common method involves the hydration of ethylene, a hydrocarbon derived from petroleum or natural gas. This process is highly efficient and allows for large-scale production, making it a popular choice in industries where high-purity ethanol is required.
But why would anyone choose synthetic ethanol over bioethanol? Well, synthetic ethanol offers several advantages, including higher purity and consistency. It’s also less dependent on agricultural resources, which can be a big deal in regions where crops are scarce or expensive. Plus, synthetic ethanol production can be fine-tuned to meet specific industrial needs, making it a go-to option for many manufacturers.
The Role of the Borosilicate Glass Reactor
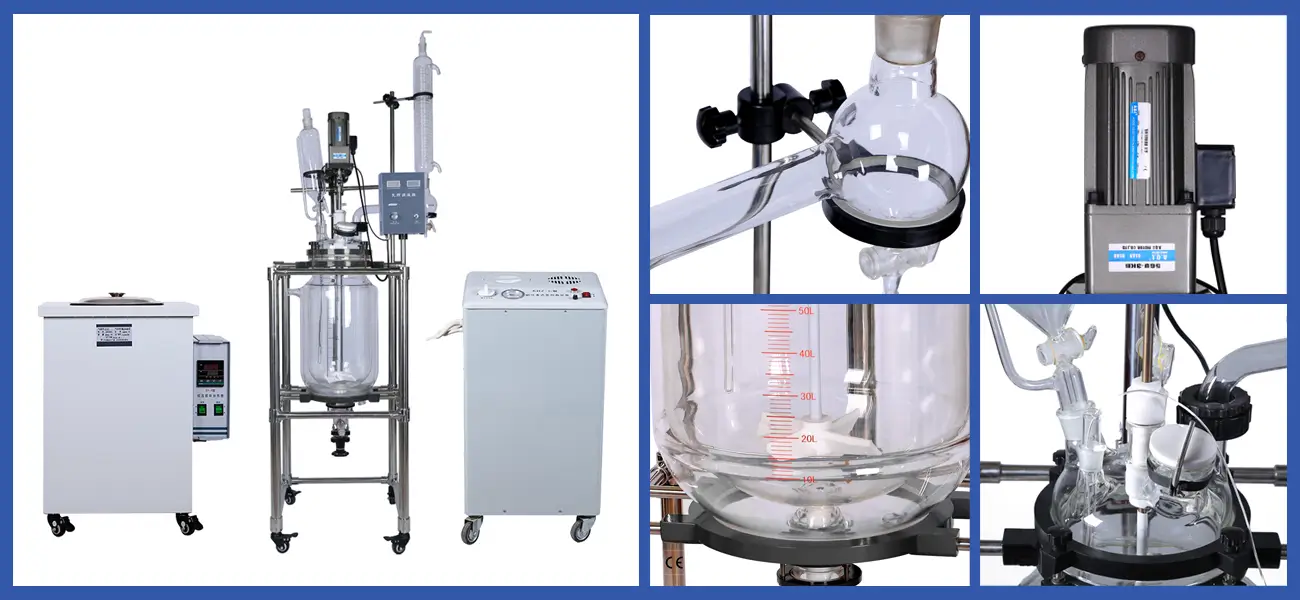
Now, let’s talk about one of the unsung heroes of synthetic ethanol production: the borosilicate glass reactor. This specialized piece of equipment is essential for carrying out the chemical reactions needed to produce ethanol. But what makes it so special?
Borosilicate glass is known for its durability and resistance to thermal shock, which means it can handle the high temperatures and pressures involved in synthetic ethanol production without cracking or breaking. It’s also chemically inert, so it won’t react with the substances inside the reactor, ensuring that the ethanol produced is of the highest purity.
Imagine trying to bake a cake in a pan that reacts with the ingredients—yuck! The same principle applies here. A borosilicate glass reactor provides a clean, stable environment for the chemical reactions to take place, which is crucial for producing high-quality ethanol.

The Chemical Process: Hydration of Ethylene
So, how does the actual process work? The synthetic production of ethanol primarily involves the hydration of ethylene. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Ethylene Supply: Ethylene, a gas derived from petroleum or natural gas, is the starting material. It’s fed into the reactor under controlled conditions.
Catalyst Introduction: A catalyst, usually phosphoric acid, is introduced to speed up the reaction. Catalysts are like the matchmakers of the chemical world—they bring reactants together without getting consumed in the process.
Hydration Reaction: Water (H₂O) is added to the ethylene (C₂H₄) in the presence of the catalyst. The reaction produces ethanol (C₂H₅OH). The chemical equation looks like this:
C2H4+H2O→C2H5OHC2H4+H2O→C2H5OH
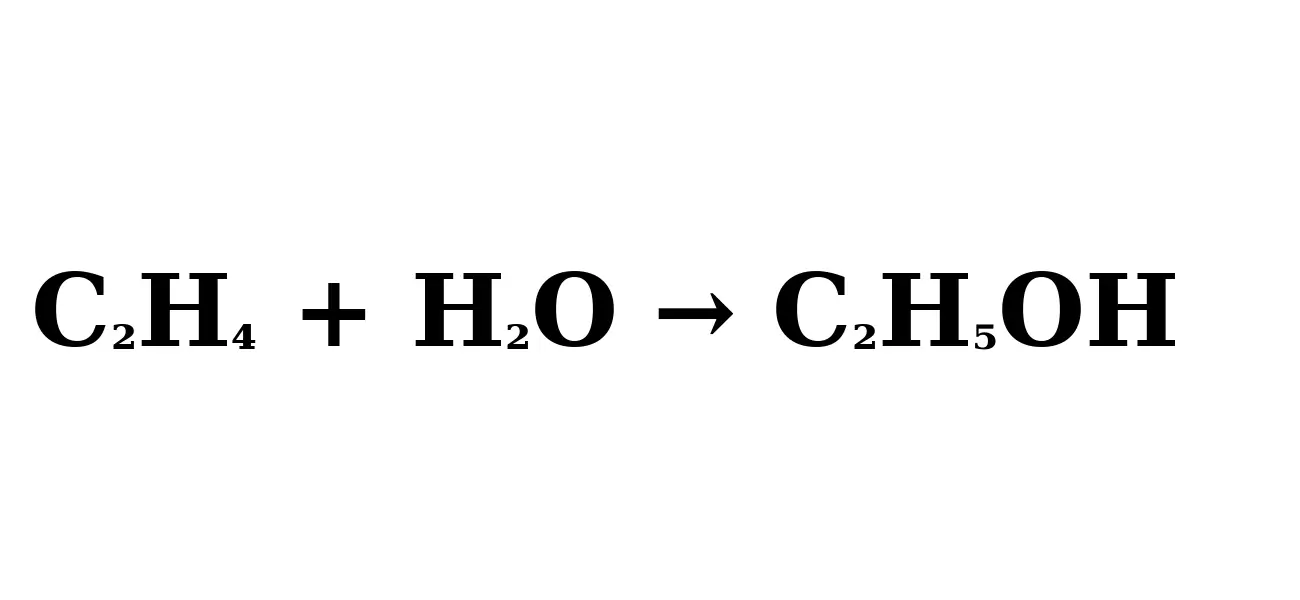
Separation and Purification: The resulting mixture contains ethanol, water, and some unreacted ethylene. The mixture is then cooled and passed through a series of distillation columns to separate the ethanol from the other components. This step ensures that the final product is as pure as possible.
Final Product: The purified ethanol is collected and can be further processed or used directly, depending on its intended application.
Why Not Just Use Fermentation?
You might be wondering, why go through all this trouble when we can just ferment sugars to produce ethanol? Great question! While fermentation is a natural and well-established method, it has its limitations. For one, it’s slower and less efficient than synthetic production. Fermentation also produces a lower concentration of ethanol, which means additional steps are needed to purify it.
On the other hand, synthetic ethanol production is faster, more scalable, and can be tailored to produce ethanol with specific properties. This makes it ideal for industrial applications where consistency and purity are paramount.
The Environmental Angle: Is Synthetic Ethanol Eco-Friendly?
Another question that often comes up is whether synthetic ethanol is environmentally friendly. The answer is a bit nuanced. On one hand, synthetic ethanol production relies on fossil fuels like petroleum and natural gas, which are non-renewable resources. This raises concerns about sustainability and carbon emissions.
However, advancements in technology are making the process more efficient and less polluting. For example, some modern facilities are using renewable energy sources to power their reactors, reducing the overall carbon footprint. Additionally, the high purity of synthetic ethanol means that less energy is required for purification, which can offset some of the environmental impact.
Saving Money Is The Last Word, And It Is Worth Investing In Buying!
When it comes to cost-effectiveness, synthetic ethanol production has a lot going for it. The process is highly efficient, and the use of catalysts like phosphoric acid helps to minimize waste. Plus, the ability to produce large quantities of high-purity ethanol in a relatively short time makes it a cost-effective option for industries that require large volumes of the chemical.
Investing in high-quality equipment, like a borosilicate glass reactor, may seem expensive upfront, but it pays off in the long run. These reactors are durable, require minimal maintenance, and can operate efficiently for years, making them a smart investment for any facility involved in synthetic ethanol production.
The Future of Synthetic Ethanol Production
As technology continues to advance, the future of synthetic ethanol production looks promising. Researchers are exploring new catalysts and reaction conditions that could make the process even more efficient and environmentally friendly. There’s also growing interest in using renewable sources of ethylene, such as bio-based ethylene, which could further reduce the environmental impact of synthetic ethanol production.
So, what’s next for synthetic ethanol? Only time will tell, but one thing is certain: as long as there’s a demand for high-purity ethanol, the synthetic production process will continue to evolve and improve.
Wrapping It Up
In conclusion, synthetic ethanol production is a complex but fascinating process that combines chemistry, engineering, and a bit of ingenuity. From the hydration of ethylene to the use of specialized equipment like borosilicate glass reactors, every step is carefully designed to produce high-quality ethanol efficiently and cost-effectively.
Whether you’re a chemist, an engineer, or just someone curious about how things are made, understanding the synthetic production of ethanol offers a glimpse into the incredible world of industrial chemistry. And who knows? Maybe the next time you fill up your car with ethanol-blended fuel or use a product that contains ethanol, you’ll appreciate the science and technology that went into making it.
So, what do you think? Could synthetic ethanol production be the key to meeting the growing demand for this versatile chemical? Or do you think bioethanol will continue to dominate the market? Let’s keep the conversation going!
